Theme: Amalgamation of innovations in Stem Cell Research
Stemcell Conference 2020
12 TH World Congress on Cell & Stem Cell Research
The success of the 11th Cell Science conferences series LLC Ltd has given us the prospect to bring the gathering one more time for our 12th World Congress 2020 meet in Prague Czech Republic, UK. Since its commencement in 2011 cell science series has perceived around 750 researchers of great potentials and outstanding research presentations around the globe. The awareness of stem cells and its application is increasing among the general population that also in parallel offers hope and add woes to the researchers of cell science due to the potential limitations experienced in the real-time.
Stem Cell Research-2020 has the goal to fill the prevailing gaps in the transformation of this science of hope to promptly serve solutions to all in the need. World Congress 2020 will have an anticipated participation of 100-120 delegates from around the world to discuss the conference goal.
History of Stem cells Research
Stem cells have an interesting history, in the mid-1800s it was revealed that cells were basically the building blocks of life and that some cells had the ability to produce other cells. Efforts were made to fertilize mammalian eggs outside of the human body and in the early 1900s, it was discovered that some cells had the capacity to generate blood cells. In 1968, the first bone marrow transplant was achieved successfully to treat two siblings with severe combined immunodeficiency. Other significant events in stem cell research include:
1978: Stem cells were discovered in human cord blood
1981: First in vitro stem cell line developed from mice
1988: Embryonic stem cell lines created from a hamster
1995: First embryonic stem cell line derived from a primate
1997: Cloned lamb from stem cells
1997: Leukaemia origin found as haematopoietic stem cell, indicating possible proof of cancer stem cells
Funding in USA:
No federal law forever did embargo stem cell research in the United States, but only placed restrictions on funding and use, under Congress's power to spend. By executive order on March 9, 2009, President Barack Obama removed certain restrictions on federal funding for research involving new lines of human embryonic stem cells. Prior to President Obama's executive order, federal funding was limited to non-embryonic stem cell research and embryonic stem cell research based upon embryonic stem cell lines in existence prior to August 9, 2001. In 2011, a United States District Court "threw out a lawsuit that challenged the use of federal funds for embryonic stem cell research”.
Members Associated with Stem Cell Research:
Discussion on Development, Regeneration, and Stem Cell Biology takes an interdisciplinary approach to understanding the fundamental question of how a single cell, the fertilized egg, ultimately produces a complex fully patterned adult organism, as well as the intimately related question of how adult structures regenerate. Stem cells play critical roles both during embryonic development and in later renewal and repair. More than 65 faculties in Philadelphia from both basic science and clinical departments in the Division of Biological Sciences belong to Development, Regeneration, and Stem Cell Biology. Their research uses traditional model species including nematode worms, fruit-flies, Arabidopsis, zebrafish, amphibians, chick and mouse as well as non-traditional model systems such as lampreys and cephalopods. Areas of research focus include stem cell biology, regeneration, developmental genetics, and cellular basis of development, developmental neurobiology, and “evo-devo” (Evolutionary developmental biology).
Stem Cell Market Value:
Worldwide many companies are developing and marketing specialized cell culture media, cell separation products, instruments and other reagents for life sciences research. We are providing a unique platform for the discussions between academia and business.
Why to attend???
Stem Cell Research-2020 could be an outstanding event that brings along a novel and International mixture of researchers, doctors, leading universities and stem cell analysis establishments creating the conference an ideal platform to share knowledge, adoptive collaborations across trade and world, and assess rising technologies across the world. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, tactics, and the newest updates in cell science fields are assurances of this conference.
A Unique Opportunity for Advertisers and Sponsors at this International event:
http://stemcell.conferenceseries.com/sponsors.php
UAS Major Universities which deals with Stem Cell Research
· University of Washington/Hutchinson Cancer Center
· Oregon Stem Cell Center
· University of California Davis
· University of California San Francisco
· University of California Berkeley
· Stanford University
· Mayo Clinic
Major Stem Cell Organization Worldwide:
· Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research
· France I-stem
· Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine Ctr, Beijing
· Stem Cell Research Centre, Korea
· NSW Stem Cell Network
· Monash University of Stem Cell Labs
· Australian Stem Cell Centre
Target Audience:
Eminent personalities, Directors, CEO, President, Vice-president, Organizations, Associations heads and Professors, Research scientists, Stem Cell laboratory heads, Post-docs, Students other affiliates related to the area of Stem cell research, stem cell line companies can be as Target Audience
Market Analysis of Stem Cell Therapy:
The global market for stem cell products was $3.8 billion in 2011. This market is expected to reach nearly $4.3 billion in 2012 and $6.6 billion by 2016, increasing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.7% from 2011 to 2016.
Americas is the largest region of global stem cell market, with a market share of about $2.0 billion in 2013. The region is projected to increase to nearly $3.9 billion by 2019, with a CAGR of 13.9% for the period of 2013 to 2019
Europe is the second largest segment of the global stem cell market and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.4% reaching about $2.4 billion by 2019 from nearly $1.4 billion in 2013.
Companies working for Stem Cells:
|
Company |
Location |
Business Type |
|
Cynata Therapeutics |
Armadale, Australia |
Stem Cell Manufacturing Technology |
|
Mesoblast |
Melbourne, Australia |
Regenerative Medicine |
|
Activartis |
Vienna, Austria |
Dendritic Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy |
|
Aposcience |
Vienna, Austria |
Treatments composed of mixture of cytokines, growth factors and other active components |
|
Cardio3 Biosciences |
Mont-Saint-Guibert, Belgium |
Stem Cell Differentiation |
|
Orthocyte (BioTime) |
Alameda, CA |
Cellular Therapies |
|
Capricor |
Beverly Hills, CA |
Stem Cell Heart Treatments |
|
Life Stem Genetics |
Beverly Hills, CA |
Autologous stem cell therapy |
|
International Stem Cell |
Carlsbad, CA |
Proprietary Stem Cell Induction |
|
Targazyme |
Carlsbad, CA |
Cell Therapy |
|
DaVinci Biosciences |
Costa Mesa, CA |
Cellular Therapies |
|
Invitrx Therapeutics |
Irvine, CA |
Autologous Stem Cell Therapy, Therapeutic & Cosmetic |
General Trends within the Stem Cell Sector
Stem Cell Software’s :
- Cryus : Cryus is developed specially for Cord Blood Banks, Donor Centers, Stem Cells Collection Centers, Biotech Laboratories and Tissue Banks.
- Label-InnThe: Which allows to record the donor or the patient personal data into the database and generates the Donation Identification Number (DIN) according to ICCBBA international standard ISBT128. It serves as labelling software for blood samples and Stem Cells products.
Products Manufactured By Industry Related to Stem Cell:
RoboSep™-16 is the latest RoboSep™ instrument ingenuous for performing fully-automated cell separation from a huge number of samples. Using EasySep™, the column-free immunomagnetic cell separation system, RoboSep™-16 isolates desired cells from a wide range of samples from different species, tissue sources or sizes using positive or negative selection. Through an intuitive user interface, the RoboSep™-16 simultaneously isolates cells from up to sixteen samples with minimal hands on time. By automating all reagent and sample handling steps, and through the use of disposable pipette tips, the RoboSep™-16 rapidly isolates all desired cells while minimizing the risk of sample cross-contamination. After completion of the cell isolation procedure, cells of interest are immediately available for any downstream application.
The EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Kit is designed to isolate highly purified CD25+ cells from single cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by positive selection. Desired cells are labeled with antibodies and magnetic particles. The cells are separated without columns using an EasySep™ magnet. Unwanted cells are simply poured off, while desired cells remain in the tube. Isolated cells are immediately ready for downstream applications such as flow cytometry, cell culture, or suppression assays.
Featured Research:
Gene therapy gives assurance for severe combined immunodeficiency, Researchers have initiated that gene therapy using a improved delivery system, or vector, can restore the immune systems of children with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID-X1), a rare, life-threatening inherited condition that primarily affects boys. Previous efforts to treat SCID-X1 with gene therapy were initially efficacious, but approximately one-quarter of the children developed leukemia two to five years after treatment. Results from a study partially funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), suggest that the new vector is equally effective at restoring immunity and may be safer than previous approaches.
References:
- http://www.stemcell.com/en/Products/All-Products/EasySep-Mouse-CD25-Regulatory-T-Cell-Positive-Selection-Kit.aspx
- http://seekingalpha.com/article/1347281-investing-in-the-stem-cell-sector-an-overview
- http://mbbnet.umn.edu/scmap/scresearchmap.html
- http://biopharmguy.com/links/company-by-location-stem-cells.php
- http://www.marketwired.com/press-release/latest-research-shows-stem-cell-product-market-to-reach-6-billion-by-2016-1688406.htm
1. Cell Signaling & Cell Communication :-
Cell signaling is part of any communication process that governs basic activities of cells and coordinates all cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity, as well as normal tissue homeostasis. Errors in signaling interactions and cellular information processing are responsible for diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding cell signaling, diseases may be treated more effectively and, theoretically, artificial tissues may be created.
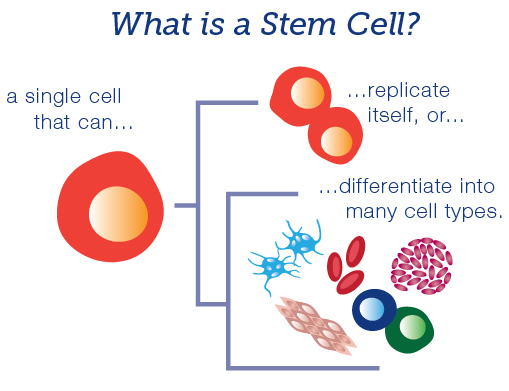
2. Stem Cells & Types:-
Stem cells: An undifferentiated cell of a multicellular organism which is capable of giving rise to indefinitely more cells of the same type, and from which certain other kinds of cell arise by differentiation. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specific cell types. The two defining characteristics of a stem cell are perpetual self-renewal and the ability to differentiate into a specialized adult cell type. There are two major classes of stem cells: pluripotent that can become any cell in the adult body, and multipotent that are restricted to becoming a more limited population of cells.
- Embryonic stem cells
- Non-embryonic (adult) stem cells
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
3. Stem Cell Epigenetics/Cell Biology.
The study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression rather than alteration of the genetic code itself. Epigenetics are stable heritable traits that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence
4. Stem Cell Niches & Bio banking :-
A stem-cell niche is an area of a tissue that provides a specific microenvironment, in which stem cells are present in an undifferentiated and self-renewable state. Cells of the stem-cell niche interact with the stem cells to maintain them or promote their differentiation. The general niche model involves the association between resident stem cells and heterologous cell types—the niche cells.
Stem Cell Banking is a facility that preserves stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use. Stem cell samples in private or family banks are preserved precisely for use by the individual person from whom such cells have been collected and the banking costs are paid by such person. The sample can later be retrieved only by that individual and for the use by such individual or, in many cases, by his or her first-degree blood relatives.
5. Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction:-
Self-reestablishment and multiplication of foundational microorganism populaces is controlled, to some degree, by affectation of apoptosis. The quantity of foundational microorganisms is thusly a harmony between those lost to separation/apoptosis and those increased through multiplication. Apoptosis of immature microorganisms is accepted to be a dynamic procedure which changes because of natural conditions.
6.Stem Cell Embryology :-
Embryonic stem (ES) cells are cells derived from the early embryo that can be propagated indefinitely in the primitive undifferentiated state while remaining pluripotent; they share these properties with embryonic germ (EG) cells. Candidate Embryonic stem and embryonic germ cell lines from the human blastocyst and embryonic gonad can differentiate into multiple types of somatic cell.her.
7. Stem Cell Embryology :-
Stem cell therapy is a type of cell therapy in which therapeutic efficacy exclusively attributed to the potency (function) of donor stem cells, presented in any quantity and purity. Bone marrow transplant is the most widely used stem-cell therapy, but some therapies derived from umbilical cord blood are also in use.
8. Stem Cell Therapies :-
Stem Cell Biomarker is characterized as a quality or their proteins that are utilized to disengage and recognize immature microorganisms. The other approach to distinguish the undifferentiated organisms is by utilizing utilitarian assays. Molecular biomarkers serve as profitable apparatuses to arrange and segregate embryonic immature microorganisms (ESCs) and to screen their separation state by immunizer based systems. ESCs can offer ascent to any grown-up cell sort and in this way offer colossal potential for regenerative medication and drug revelation. Various biomarkers, for example, certain cell surface antigens, are utilized to dole out pluripotent ESCs .
9. Diseases and Stem Cell Treatment :-
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition.The most well-established and widely used stem cell treatment is the transplantation of blood stem cells to treat diseases and conditions of the blood and immune system, or to restore the blood system after treatments for specific cancers.
10.Stem Cells technology :-
- Protection of human stem cells
- Stem cell and insulin
- Hematopoietic malignancies
- Immune cells regulate blood stem cells
11.Re-Evaluating Strategies for Transplantation of stem cells :-
Stem cell transplantation, sometimes referred to as bone marrow transplant, is a procedure that replaces unhealthy blood-forming cells with healthy cells. Stem cell transplants commonly are used to treat Leukemia and lymphoma, cancers that affect the blood and lymphatic system..
12. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine :-
Tissue engineering can be defined as the use of a combination of cells, engineering materials, and suitable biochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions in an effort to improve clinica l procedures for the repair of damaged tissues and organs.
13. Disease Modelling and Drug Discovery :-
A disease model is an animal or cells displaying all or some of the pathological processes that are observed in the actual human or animal disease. Studying disease models aids understanding of how the disease develops and testing potential treatment approaches.
14. Tumour cell science :-
Cancer cells are cells gone wrong in other words, they no longer respond to many of the signals that control cellular growth and death. Cancer cells originate within tissues and, as they grow and divide, they diverge ever further from normalcy. Over time, these cells become increasingly resistant to the controls that maintain normal tissue and as a result, they divide more rapidly than their progenitors and become less dependent on signals from other cells. Cancer cells even evade programmed cell death, despite the fact that their multiple abnormalities would normally make them prime targets for apoptosis. In the late stages of cancer, cells break through normal tissue boundaries and metastasize to new sites in the body
15. Applications in Nanotechnology :-
- Nanotechnology In The Regeneration of Complex Tissues
- Regenerative Approaches With Nanoparticles
16. Cellular Plasticity And Reprogramming :-
Stem cell plasticity refers to the ability of some stem cells to give rise to cell types, formerly considered outside their normal repertoire of differentiation for the location where they are found. Included under this umbrella title is often the process of “transdifferentiation” – the conversion of one differentiated cell type into another, and metaplasia – the conversion of one tissue type into another.
17. Cell And Organ Regeneration :-
Regenerative medicine is a branch of translational research in tissue engineering and molecular biology which deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function.
18. Cell and Gene Therapy :-
Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. In the future, this technique may allow doctors to treat a disorder by inserting a gene into a patient’s cells instead of using drugs or surgery.
19. Stem Cells and Veterinary Applications :-
The stem cell field in veterinary medicine continues to evolve rapidly both experimentally and clinically. Stem cells are most commonly used in clinical veterinary medicine in therapeutic applications for the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries in horses and dogs. New technologies of assisted reproduction are being developed to apply the properties of spermatogonial stem cells to preserve endangered animal species.same methods can be used to generate transgenic animals for production of pharmaceuticals or for use as biomedical models.
20. Clinical Trials on Cell & Gene Therapy :-
Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. In the future, this technique may allow doctors to treat a disorder by inserting a gene into a patient’s cells instead of using drugs or surgery.
21. Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues :-
The regulation of stem cell research is an issue that has drawn much comment, criticism and even judicial arbitration in recent years.
- Ethical Issues In Stem Cell Research
- Key Ethical Issues In Embryonic Stem Cell
- IPR
- Biosafety And rDNA Guidelines
- Governing Stem Cell Therapy And Fundings
22. Molecular Medicine:-
Molecular medicine is a broad field, where physical, chemical, biological, bioinformatics and medical techniques are used to describe molecular structures and mechanisms, identify fundamental molecular and genetic errors of disease, and to develop molecular interventions to correct them.
Conference Highlights
- Cell Signaling & Cell Communication
- Stem Cells & Types
- Stem Cell Epigenetics
- Stem Cell Niches & Bio banking
- Stem Cell Apoptosis and Signal Transduction
- Stem Cell Embryology
- Stem Cell Therapies
- Stem Cell Biomarkers
- Disease Modelling and Drug Discovery
- Stem Cells technology
- Re-Evaluating Strategies for Transplantation of stem cells
- Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
- Novel Technologies
- Diseases and Stem Cell Treatment
- Tumour cell science
- Applications in Nanotechnology
- Cellular Plasticity And Reprogramming
- Cell And Organ Regeneration
- Cell and Gene Therapy
- Clinical Trials on Cell & Gene Therapy
- Stem Cells and Veterinary Applications
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues
- Stem Cell Market World Wide
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 15-16, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Cell Science & Therapy
- https://www.omicsonline.org/cell-science-therapy.php
- https://www.omicsonline.org/cell-science-therapy.php
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by




